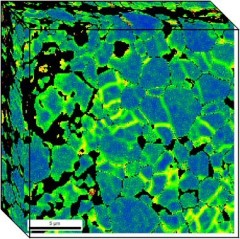
Ferrite-martensite dual phase (DP) steels
The term “dual-phase steel” refers to a group of steels consisting of a soft ferrite matrix and 3–30 vol.% of hard martensite islands. These steels are widely used for automotive applications. DP
steels have a number of
unique properties, which include a low elastic limit, high initial strain-hardening rate, continuous yielding, high tensile strength and high uniform and total elongation. Moreover, DP steels exhibit
a bake-hardening (BH) effect, i.e.
the yield strength increases upon aging at paint-baking temperatures (ca. 170 °C) after forming, giving rise to improved dent and crush resistance. The austenite-to-martensite phase transformation
bears the main influence on the
mechanical properties of dual-phase steels. This phase transformation involves a volume expansion of 2–4%, causing an elastically and plastically deformed zone in the ferrite adjacent to
martensite.
International Journal of Plasticity 63 (2014) 198-210:
Ferritic–martensitic dual phase (DP) steels deform spatially in a highly heterogeneous
manner, i.e. with strong strain and stress partitioning at the micro-scale. Such heterogeneity in local strain evolution leads in turn to a spatially heterogeneous damage distribution, and thus, plays an important role in the process of damage inheritance and fracture. To understand and improve DP steels, it is important to identify connections between the observed strain and damage heterogeneity and the underlying microstructural parameters, e.g. ferrite grain size, martensite distribution, martensite fraction, etc. In this work we pursue this aim by conducting in-situ deformation experiments on two different DP steel grades, employing two differ
Int Journ Plast 2014 Tasan Roters Diehl [...]
PDF-Dokument [1.9 MB]
Acta Mater 59 (2011) 658 DP steel aging [...]
PDF-Dokument [1.8 MB]
The mechanical response of multiphase alloys is governed by the microscopic strain and stress partitioning behavior among microstructural constituents. However, due to limitations in the characterization of the partitioning that takes place at the submicron scale, microstructure optimization of such alloys is typically based on evaluating the averaged response, referring to, for example, macroscopic stress–strain curves. Here, a novel experimental–numerical methodology is introduced to strengthen the integrated understanding of the microstructure and mechanical properties of these alloys, enabling joint analyses of deformation-induced evolution of the microstructure, and the strain and stress distribution therein, down to submicron resolution. From the experiments, deformation-induced
Acta Materialia 2014 CPFEM ICME DP steel[...]
PDF-Dokument [6.6 MB]
Acta-Materialia-2013-recrystallization a[...]
PDF-Dokument [966.7 KB]
Experimental and numerical investigation of geometrically necessary dislocations (GND) and non-homogeneous mechanical properties of the ferrite phase in dual phase steels
Acta Mater 2011 dual phase steel GND sim[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.7 MB]
2012_Metall-Trans-Mn-effeect-on-DP-steel[...]
PDF-Dokument [971.0 KB]
Mater_Science_Engin_A 527 (2010) 2738.pd[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.2 MB]
ISSS09_Calcagnotto.pdf
PDF-Dokument [2.5 MB]
DP_MSE-A_2010.pdf
PDF-Dokument [870.4 KB]
A novel Mn-based 1 GPa duplex stainless TRIP steel with 60% ductility by a reduction of austenite stability
Acta Materialia 59 (2011) 4653–Mn-duplex[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.5 MB]
Experimental and numerical study on geometrically
necessary dislocations and non-homogeneous mechanical properties of the ferrite phase in dual phase steels
Acta-Mater-2011-DP-GND-simulation.pdf
PDF-Dokument [1.7 MB]