Atom probe tomography on complex materials
Acta Materialia 92 (2015) 33-45
Atom probe informed simulations of dislocation–precipitate interactions reveal the importance of local interface curvature
A. Prakash, J. Guenole, J. Wang, J. Müller, E. Spiecker, M.J. Mills, I. Povstugar, P. Choi, D. Raabe and E. Bitzek
Acta Materialia 92 (2015) 33 Atom probe [...]
PDF-Dokument [1.8 MB]
Elemental partitioning and mechanical properties of Ti- and Ta-containing Co–Al–W-base superalloys studied by atom probe tomography and nanoindentation
Ivan Povstugar, Pyuck-Pa Choi,Steffen Neumeier, Alexander Bauer, Christopher H. Zenk, Mathias Goken, Dierk Raabe
Acta Mater 2014 Co base superalloy atom [...]
PDF-Dokument [768.8 KB]
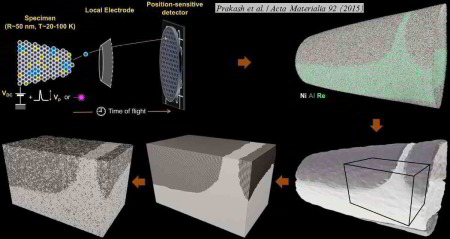
The interaction of dislocations with precipitates is an essential strengthening mechanism in metals, as exemplified by the superior high- temperature strength of Ni-base superalloys. Here we use atomistic simulation samples generated from atom probe tomography data of a single crystal superalloy to study the interactions of matrix dislocations with a gamma' precipitate in molecular dynamics simulations. It is shown that the precipitate morphology, in particular its local curvature, and the local chemical composition significantly alter both, the misfit dislocation network which forms at the precipitate interface, and the core structure of the misfit dislocations. Simulated tensile tests reveal the atomic scale details of many experimentally observed dislocation–precipitate interaction mechanisms, which cannot be reproduced by idealized simulation setups with planar interfaces. We thus demonstrate the need to include interface curvature in the study of semicoherent precipitates and introduce as an enabling method atom probe tomography-informed atomistic simulations.
PRL 113, 035501 (2014) PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
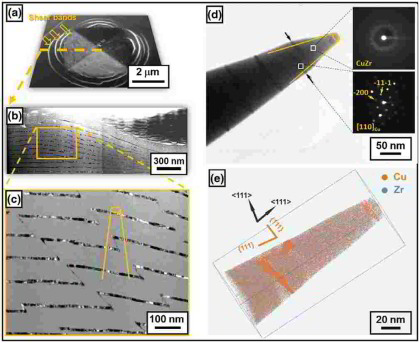
Deformation of ductile crystalline-amorphous nanolaminates is not well understood due to the complex interplay of interface mechanics, shear banding, and deformation-driven chemical mixing. Here we present indentation experiments on 10 nm nanocrystalline Cu–100 nm amorphous CuZr model multilayers to study these mechanisms down to the atomic scale. By using correlative atom probe tomography and transmission electron microscopy we find that crystallographic slip bands in the Cu layers coincide with noncrystallographic shear bands in the amorphous CuZr layers. Dislocations from the crystalline layers drag Cu atoms across the interface into the CuZr layers. Also, crystalline Cu blocks are sheared into the CuZr layers. In
these sheared and thus C
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS vol 113 - page 0[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.1 MB]
PRL 113, 106104 (2014) PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
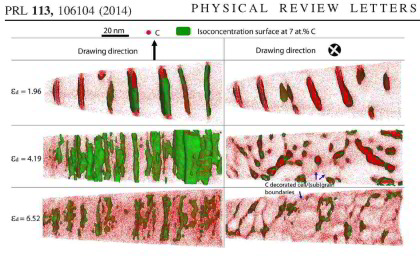
Grain refinement through severe plastic deformation enables synthesis of ultrahigh-strength nanostructured materials. Two challenges exist in that context: First, deformation-driven grain refinement is limited by dynamic dislocation recovery and crystal coarsening due to capillary driving forces; second, grain boundary sliding and hence softening occur when the grain size approaches several nanometers. Here, both challenges have been overcome by severe drawing of a pearlitic steel wire (pearlite: lamellar structure of alternating iron and iron carbide layers). First, at large strains the carbide phase dissolves via mechanical alloying, rendering the initially two-phase pearlite structure into a carbon-supersaturated iron phase. This carbon-ric
Phys Rev Lett vol 113 page 106104 (2014)[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.2 MB]
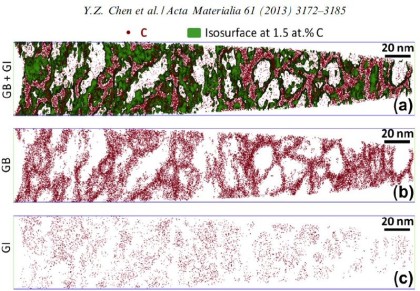
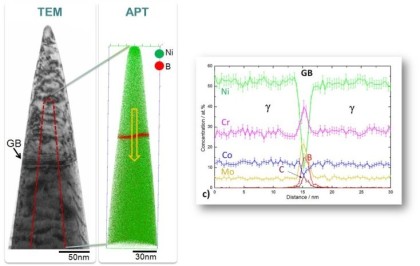
Grain boundary segregation leads to nanoscale chemical variations that can alter a material's performance by orders of magnitude. To understand this phenomenon, a large number of grain boundaries is p
PhysRevLett.112.126103.pdf
PDF-Dokument [842.8 KB]
B2 NiMn and Ni2MnAl Heusler nanoprecipitates are designed via elastic misfit stabilization in Fe–Mn maraging steels by combining transmission electron microscopy (TEM) correlated atom probe tomography (APT) with ab initio simulations.
Acta Mater 2014 Fe-Mn maraging steel Heu[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.6 MB]
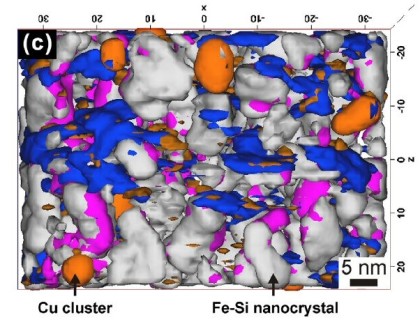
Rapid annealing (4–10 s) induced primary crystallization of soft magnetic Fe–Si nanocrystals in a Fe73.5Si15.5Cu1Nb3B7 amorphous alloy has been systematically studied by atom probe tomography in c
Acta Mater FeSiNbBCu nanocrystalline mag[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.6 MB]
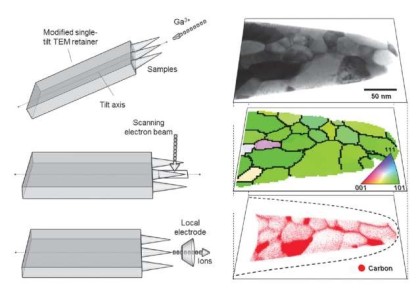
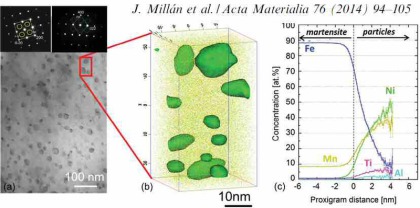
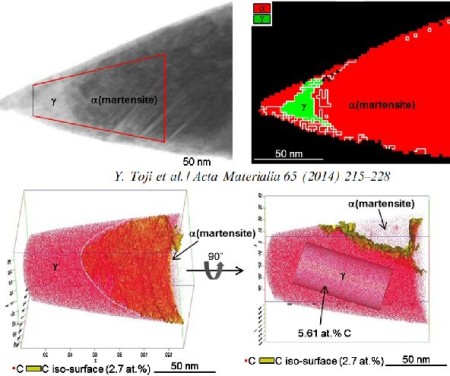
Carbon partitioning is investigated by means of atom probe tomography and correlative transmission electron microscopy. A model steel (Fe–0.59 wt.% C (2.7 at.% C)–2.0 wt.% Si–2.9 wt.% Mn) with m
Acta Mater 2014 carbon partitioning mart[...]
PDF-Dokument [4.0 MB]
2013-Acta-Nanocrystalline Fe–C alloys by[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.1 MB]
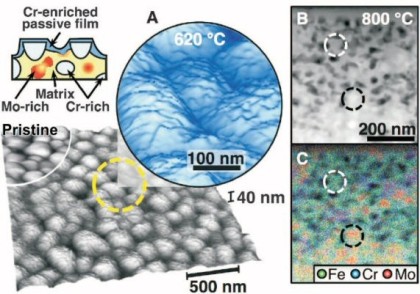
Ultrathin passive films effectively prevent the chemical attack of stainless steel grades in corrosive environments; their stability depends on the interplay between structure and chemistry of the con
Science-2013-Duarte-372-6.pdf
PDF-Dokument [1.7 MB]
Characterization of high carbon bearing steel 100Cr6 using electron microscopy
and atom probe tomography in combination with multi-component diffusion simulations.
partitioning carbide atom probe tomograp[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.1 MB]
Compound semiconductors belong to the most important materials for optoelectronic applications. Full understanding of the properties of compound semiconductor devices requires quantitative composition
Microscopy Today 2012 atom probe analysi[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.9 MB]
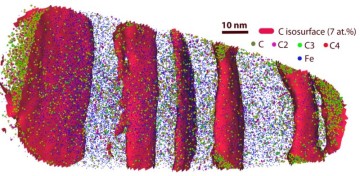
APT-TiAlN-CrN multilaerys Acta-2013.pdf
PDF-Dokument [3.5 MB]
In pearlitic steel wires dissociation of cementite occurs during deformation. Here we study the influence of carbide decomposition on the diffusion of nickel in ferrite by atom probe tomography.
2013-Scripta-Kresse-diffusion of Ni in fe[...]
PDF-Dokument [353.5 KB]
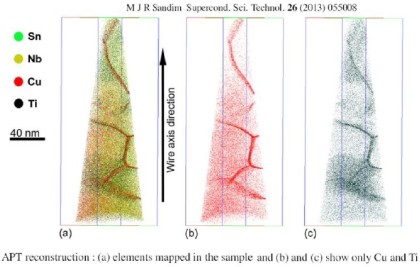
We study grain boundary segregation in a bronze-route Nb3Sn superconducting wire
by atom probe tomography.
Supercond. Sci. Techno. 26 (2013) 05500R[...]
PDF-Dokument [5.3 MB]
Atomic-scale investigation of e and h precipitates in bainite in 100Cr6 bearing steel by atom probe tomography and ab initio calculations
atom probe tomography bearing steel 100C[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.8 MB]
In an Fe–9 at.% Mn maraging alloy annealed at 450 C reversed allotriomorphic austenite nanolayers appear on former Mn decorated lath martensite boundaries. The austenite films are 5–15 nm thick an
Acta-Mater-2013-Nanoscale-austenite-form[...]
PDF-Dokument [6.0 MB]
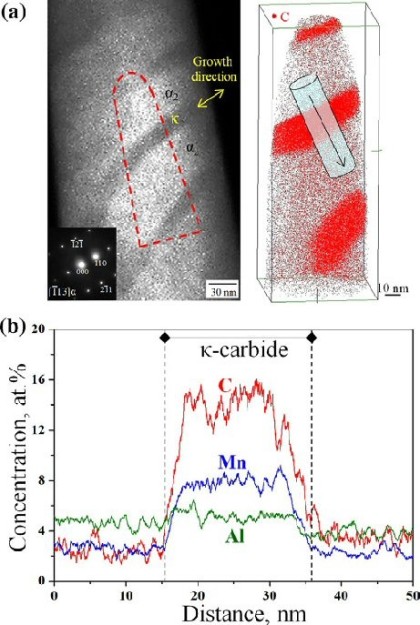
We study the structure and chemical composition of the j-carbide formed as a result of isothermal transformation in an Fe–3.0Mn–5.5Al–0.3C alloy using transmission electron microscopy and APT:
Scripta-kappa-carbides-in-steel.pdf
PDF-Dokument [1.0 MB]
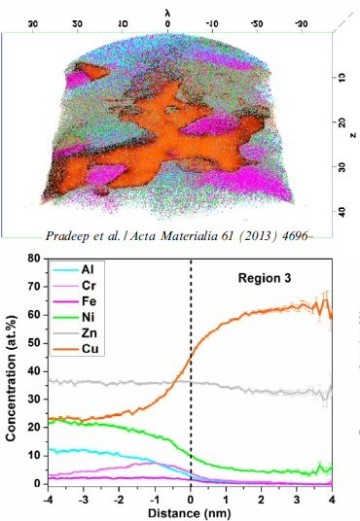
Acta Materialia 61 (2013) 4696–4706
Acta-Materialia-2013-atom-probe-high-ent[...]
PDF-Dokument [6.1 MB]
Development of micro- and nanostructure of a Ni-based superalloy (alloy 617B) at 700 °C analysed by electron microscopy and atom probe tomography (LEAP HX)
2012_Acta-Mater-alloy-617.pdf
PDF-Dokument [2.4 MB]
Raabe_Hono_Acta Materialia 57 (2009) 525[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.7 MB]
Metals_at_extremes-MRS_Bulletin-Dec2010.[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.2 MB]
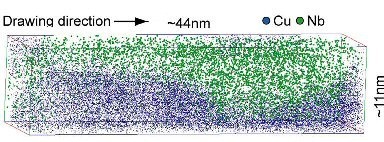
Atomistic mechanisms of deformation-induced
cementite decomposition in wire drawn pearlite
pearlite_decomposition_Acta_Materialia_2[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.8 MB]
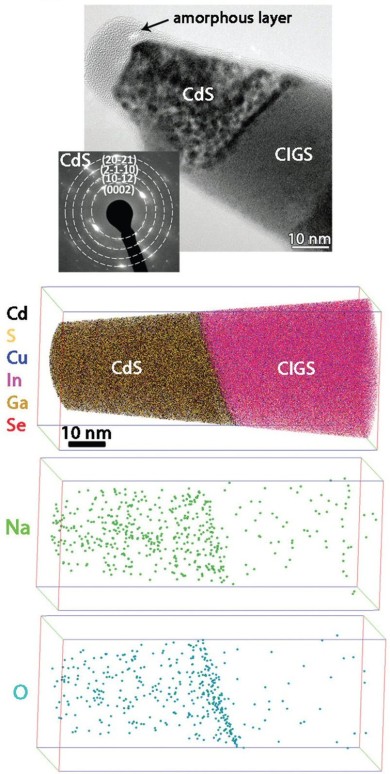
Here we study the CdS/Cu(In,Ga)Se2 p-n junction region in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells using atom probe tomography. A Cu-, Ga-depleted, and Cd-doped region of about 1 nm thickness is detected at
Appl-Phys-Letters-2012-pn junction in Cu[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.2 MB]
Evolution of strength and microstructure during annealing of heavily cold-drawn 6.3 GPa hypereutectoid pearlitic steel wire
Acta mater Vol 60 2012-heat treated pear[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.7 MB]
Atom probe tomography characterization of heavily cold drawn pearlitic steel wire
ULTRAM11133.pdf
PDF-Dokument [611.4 KB]
2011_Acta_Materialia_APT_Steel-Fe-Mn.pdf
PDF-Dokument [2.3 MB]
Metals_at_extremes-MRS_Bulletin-Dec2010_[...]
PDF-Dokument [5.5 MB]
PDF-Dokument [2.1 MB]
Journ_of_Physics_ConfSeries_326_012029_2[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.0 MB]
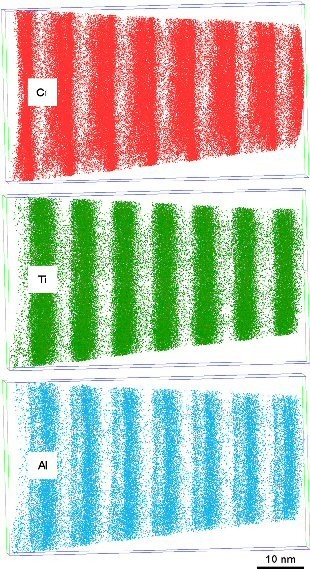
Thermal stability of TiAlN/CrN multilayer coatings studied by atom probetomography
1-s2.0-S0304399110003025-main.pdf
PDF-Dokument [3.1 MB]
Acta-2012-Austenite-reversion-Fe-Cr-C.pd[...]
PDF-Dokument [2.9 MB]
Atomic-Scale composition and structures of steels analyzed by atom probe tomography
2012_Steel_Atom-probe_Microscopy-Today.p[...]
PDF-Dokument [1.4 MB]
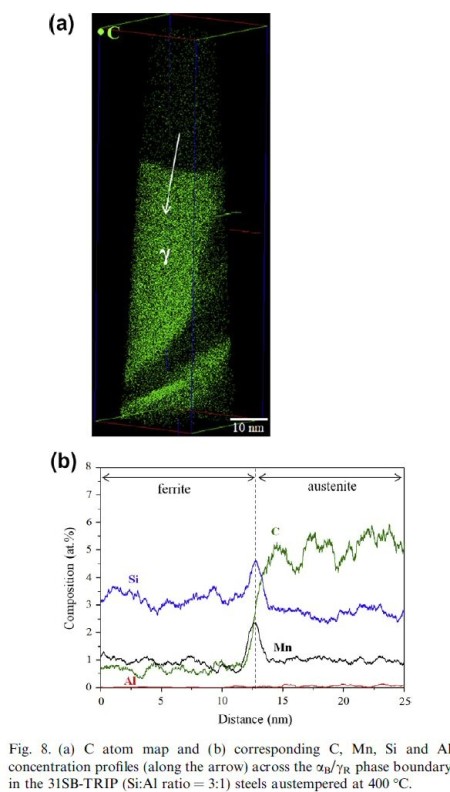
Understanding alloying and thermal processing at an atomic scale is essential for the optimal design of high-carbon (0.71 wt.%) bainitic–austenitic transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steels. W
2012-Acta-Mater-Bainite-Austenite.pdf
PDF-Dokument [3.2 MB]
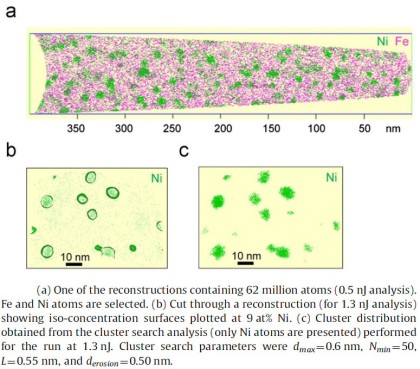
A precipitation hardened maraging TRIP steel was analyzed using a pulsed laser atom probe. The laser pulse energy was varied from 0.3 to 1.9 nJ to study its effect on the measured chemical composition
APT-ultramicroscopy-TRIP steel.pdf
PDF-Dokument [930.5 KB]